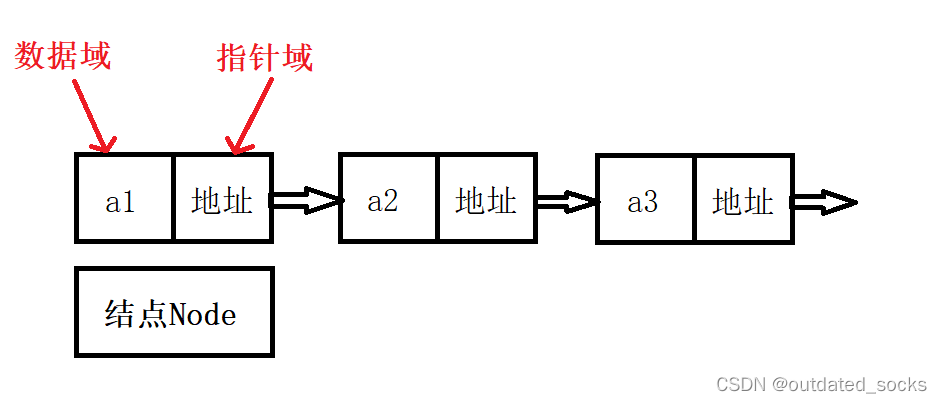
这里特指无哨兵位单向非循环链表
目录
背景
概念
单链表的实现
前景提示
单链表的结构体定义
单链表的打印
关于为什么不断言phead
关于单链表的逻辑结构和物理结构
单链表的尾插
关于为什么要用到二级指针
关于尾插的本质
关于找尾整个过程的解释
关于为什么打印单链表就不需要传二级指针
单链表的动态申请结点
单链表的头插
单链表的尾删
单链表的头删
链表的查找
单链表在pos位置之前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
单链表删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
单链表在pos位置之后插入x
单链表删除pos位置之后的值
关于不传头指针如何在pos前插入/删除(巧思)
单链表的销毁
总代码(想直接看结果的可以看这里)
背景
上一篇文章我们学习了顺序表。
但顺序表要求的是连续的物理空间,这就导致了其有以下几个缺点:
1. 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)。2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
概念
链表是一种 物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的 逻辑顺序是通过链表 中的 指针链接次序实现的 。链表中一个数据存一个内存块。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的 数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的 指针域。
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组 地址任意的存储单元(这组存储单元既可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)存放线性表中的数据元素。链表中的数据是以 结点( 每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。)来表示的,每个结点的构成: 元素+指针,元素就是存储数据的 存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的 地址数据。单链表中每个结点的存储地址是存放在其前趋结点 next 域中,而开始结点无前趋,故设头指针head指向开始结点。链表由头指针 唯一确定,单链表可以用头指针的名字来命名,终端结点无后继,故终端结点的指针域为空,即NULL。
单链表的实现
前景提示
SList.h 用于 引用的头文件、单链表的定义、函数的声明。
SList.c 用于 函数的定义。
Test.c 用于 链表功能的测试。
单链表的结构体定义
在SList.h下
- #pragma once//使同一个文件不会被包含(include)多次,不必担心宏名冲突
-
- //先将可能使用到的头文件写上
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include<assert.h>
-
- typedef int SLTDataType;//假设结点的数据域类型为 int
-
- //单链表的结构体定义
- typedef struct SListNode
- {
- SLTDataType data;//结点的数据域,用来存储数据元素
- struct SListNode* next;//结点的指针域,用来存储下一个结点地址的指针域
- //next的意思就是下一个结点的指针,上一个结点存的是下一个结点的地址
- //每个结点都是结构体指针类型
- //有些人会把上一行代码写成SListNode* next;这是不对的,因为C语言中
- //struct SListNode 整体才是一个类型(但C++可以)
- //或者写成SLTNode* next;这也是错的,因为编译器的查找规则是从上忘下找
- }SLTNode;
单链表的打印
要理解单链表,首先我们先写一个单链表的打印。
在SList.h下
- //链表的打印——助于理解链表
- void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
- #include "SList.h"//别忘了
-
- //链表的打印
- void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
- {
- //assert(phead);这里并不需要断言phead不为空
- //为什么这里不需要断言phead?
- //空链表可以打印,即phead==NULL可以打印,直接断言就不合适了
- //那空顺序表也可以打印,那它为什么就要断言呢?
- //因为phead是指向第一个存有数据的结点的
- //而顺序表的ps是指向一个结构体
- SLTNode* cur = phead;//将phead赋值给cur,所以cur也指向第一个结点
- while (cur != NULL)//或while(cur)
- {
- printf("%d->", cur->data);//打印的时候加了个箭头更方便理解
- cur = cur->next;//next是下一个结点的地址
- //++cur/cur++;这种是不行的,指针加加,加到的是连续的下一个位置
- //链表的每一个结点都是单独malloc出来的,我们不能保证结点之间的地址是连续的
- }
- printf("NULL\n");
- }
关于为什么不断言phead


关于单链表的逻辑结构和物理结构





在打印之前,我们得先有数据
单链表的尾插
在SList.h下
- // 单链表尾插
- void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
- //用二级指针,解释看下文,x为要插入的数据
关于为什么要用到二级指针


在SList.c下
- // 单链表尾插
- void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
- //注意区分几个断言的判断,plist有可能是空,pphead一定不能为空
-
- SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//先创建个结点
- if (newnode == NULL)//如果malloc失败
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- return;
- }
- //如果malloc成功
- newnode->data = x;//插入的数据
- newnode->next = NULL;//初始化为空
- //找尾(尾插之前先找到尾)
- if (*pphead == NULL)//若链表为空
- {
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
- else//若链表不为空
- {
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)//对于不为空的链表:尾插的本质
- //是原尾结点要存新尾结点的地址
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail->next = newnode;
- /*有些同学会写成:
- while (tail != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail = newnode;*/
- }
- }
关于尾插的本质


而

关于找尾整个过程的解释

↓

↓

在Test.c下
- #include "SList.h"//别忘了
-
- //用于函数功能的测试
- void TestSList1()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
-
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList1();
- return 0;
- }
关于为什么打印单链表就不需要传二级指针
因为打印单链表没有改变指针。如果要改变传过去的指针(实参),那就要传实参的地址,不改变就不传。
单链表的动态申请结点
要写头插时,我们发现不管是尾插和头插都要动态申请一个结点,所以我们可以先写一个函数来复用。
在SList.c下
- // 动态申请一个结点
- SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x)
- {
- //同样不需要断言
- SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//先创建个结点
- if (newnode == NULL)//如果malloc失败
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- return NULL;
- }
- //如果malloc成功
- newnode->data = x;//插入的数据
- newnode->next = NULL;//初始化为空
-
- return newnode;//返回newnode
- }
-
- // 单链表尾插
- void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- //找尾(尾插之前先找到尾)
- if (*pphead == NULL)//若链表为空
- {
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
- else//若链表不为空
- {
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- //对于不为空的链表:尾插的本质是原尾结点要存新尾结点的地址
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail->next = newnode;
- /*有些同学会写成:
- while (tail != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail = newnode;*/
- }
- }
单链表的头插
在SList.h下
- // 单链表的头插
- void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
在SList.c下

- // 单链表的头插
- void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- //发现plist不管是否为空,头插的方法都一样
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- newnode->next = *pphead;
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
在Test.c下
- void TestSList1()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
-
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- void TestSList2()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
-
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList1();
- TestSList2();
- return 0;
- }

单链表的尾删
尾删是否需要二级指针?要!
在SList.h下
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
在Test.c下
- void TestSList2()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList2();
- return 0;
- }
在SList.c下
有些人一开始会这样写:
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- free(tail);
- tail = NULL;
- }
结果是:

出现随机值——>很有可能是因为野指针。
 →
→
为什么呢?

这里给更改后的SList.c的两种方法
法一:

- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //法一:
- SLTNode* prev=NULL;
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- {
- prev = tail;
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- free(tail);
- tail = NULL;
- prev->next = NULL;
- }
法二:

- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //法二:
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
-
- free(tail->next);
- tail->next = NULL;
- }

但是我们再多测试几组
在Test.c下
- void TestSList2()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //尾删四个数据
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList2();
- return 0;
- }
结果:
 两方法最后都还剩一个!
两方法最后都还剩一个!
原因是未考虑到只有一个结点或没有结点的情况。

这里是再次更改后的SList.c
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //检查有无结点
- assert(*pphead != NULL);
- //1.只有一个结点
- if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
- {
- free(*pphead);
- *pphead = NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- //2.有多个结点
- /*//法一:
- SLTNode* prev=NULL;
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- {
- prev = tail;
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- free(tail);
- tail = NULL;
- prev->next = NULL;*/
- //法二:
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
-
- free(tail->next);
- tail->next = NULL;
- }
- }
只有一个结点
没有结点
单链表的头删
在SList.h下
- // 单链表头删
- void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
在SList.c下

- // 单链表头删
- void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- //检查有无结点
- assert(*pphead != NULL);
-
- SLTNode* first = *pphead;
- *pphead = first->next;
- free(first);
- first = NULL;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList3()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList3();
- return 0;
- }

链表的查找
在SList.h下
- // 单链表查找
- SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
在SList.c下
- // 单链表查找
- SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- SLTNode* cur = phead;//用cur去遍历,不用phead
- while (cur)//找x
- {
- if (cur->data == x)//如果找到了
- {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- return NULL;//如果找不到
- }
在Test.c下
- void TestSList4()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //将寻找和修改结合
- //eg:值为2的结点*2
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- ret->data *= 2;
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList4();
- return 0;
- }

单链表在pos位置之前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
在SList.h下
- //单链表在pos位置之前插入x(效率较低)(得传头指针)(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
在SList.c下

- //单链表在pos位置之前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- assert(pos);//默认pos一定会找到
- if (pos == *pphead)//如果pos在第一个位置——那就是头插
- {
- SLTPushFront(pphead, x);
- }
- else//如果pos不是第一个位置
- {
- //找到pos的前一个位置
- SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
- while (prev->next != pos)
- {
- prev = prev->next;
- }
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- prev->next = newnode;
- newnode->next = pos;
- }
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList5()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //寻找值为2的结点
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertBefore(&plist, ret, 20);//在该结点前插入值为20的结点
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList5();
- return 0;
- }

单链表删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
在SList.h下
- // 单链表删除pos位置之前的值(效率较低)(得传头指针)(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
在SList.c下
- // 单链表删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- assert(pos);
-
- if (*pphead == pos)//如果pos在第一个位置
- {
- SLTPopFront(pphead);//头删
- }
- else//如果不在第一个位置
- {
- SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
- while (prev->next != pos)
- {
- prev = prev->next;
- }
- prev->next = pos->next;
- free(pos);
- //pos = NULL;形参的改变不影响实参,加不加这句话都可以
- }
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList6()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //寻找值为2的结点
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseBefore(&plist, ret);
- ret = NULL;//一般在这里置空
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList6();
- return 0;
- }

单链表在pos位置之后插入x
在SList.h下
- // 单链表在pos位置之后插入x,单链表比较适合这种
- void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
在SList.c下
有些人会这样写:
- //单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- pos->next = newnode;
- newnode->next=pos->next;
- }
后果:

所以橙色和紫色的两步应该互换位置
更改后的SList.c
- //单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- newnode->next = pos->next;
- pos->next = newnode;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList7()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertAfter(ret, 20);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList7();
- return 0;
- }

单链表删除pos位置之后的值
在SList.h下
- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值,单链表比较适合这种
- void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
在SList.c下

- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
- void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- assert(pos->next);
-
- SLTNode* del = pos->next;//保存要删除的结点
- pos->next = pos->next->next;//或者写成pos->next=del->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList8()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseAfter(ret);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList8();
- return 0;
- }
关于不传头指针如何在pos前插入/删除(巧思)
插入:先利用单链表在pos位置之后插入x的函数,再交换pos和pos->next的值。

在SList.h下
- // 不传头指针,在pos前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore1(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
在SList.c下
- // 不传头指针,在pos前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore1(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
-
- //调用单链表在pos位置之后插入x的函数
- SLTInsertAfter(pos, x);
- //交换pos和pos->next的值
- SLTDataType temp;
- temp = pos->data;
- pos->data = pos->next->data;
- pos->next->data = temp;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList9()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertBefore1(ret,20);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList9();
- return 0;
- }
删除:先将pos->next的值赋给pos,再利用单链表删除pos位置之后的值的函数。(但此方法不能尾删)
 在SList.h下
在SList.h下
- // 不传头指针,删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore1(SLTNode* pos);
在SList.c下
- // 不传头指针,删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore1(SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- assert(pos->next);//不能尾删
- SLTNode* del = pos->next;
- pos->data = pos->next->data;
- pos->next = pos->next->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList10()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseBefore1(ret);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList10();
- return 0;
- }

单链表的销毁
方法一(不传二级指针):
在SList.h下
- // 单链表的销毁,不传二级
- void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead);
在SList.c下
- // 单链表的销毁
- void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead)
- {
- SLTNode* cur = phead;
- /*//有些人一开始会这样写
- while (cur)
- {
- //free不是销毁这个指针指向的内存,而是将指针指向的内存还给操作系统
- free(cur);//cur依旧指向free之前的地址
- cur = cur->next;
- }*/
-
- while (cur)
- {
- SLTNode* tmp = cur->next;
- free(cur);
- cur = tmp;
- }
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList11()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTDestroy(plist);
- plist = NULL;
- }
-
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList11();
- return 0;
- }
方法二(传二级指针):
在SList.h下
- // 单链表的销毁,传二级
- void SLTDestroy1(SLTNode** pphead);
在SList.c下
- // 单链表的销毁,传二级
- void SLTDestroy1(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
- while (cur)
- {
- SLTNode* tmp = cur->next;
- free(cur);
- cur = tmp;
- }
- *pphead = NULL;
- }
在Test.c下
- TestSList12()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTDestroy1(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- TestSList12();
- return 0;
- }
总代码(想直接看结果的可以看这里)
在SList.h下
- #pragma once//使同一个文件不会被包含(include)多次,不必担心宏名冲突
-
- //先将可能使用到的头文件写上
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include<assert.h>
-
- typedef int SLTDataType;//假设结点的数据域类型为 int
-
- // 单链表的结构体定义
- //↓结点 单链表 Singly Linked List
- typedef struct SListNode
- {
- SLTDataType data;//结点的数据域,用来存储数据元素
- struct SListNode* next;//结点的指针域,用来存储下一个结点地址的指针域
- //next的意思就是下一个结点的指针,上一个结点存的是下一个结点的地址
- //每个结点都是结构体指针类型
- //有些人会把上一行代码写成SListNode* next;
- //这是不对的,因为C语言中 struct SListNode 整体才是一个类型(但C++可以)
- //或者写成SLTNode* next;这也是不对的,因为编译器的查找规则是从上忘下找
- }SLTNode;
-
-
- // 链表的打印——助于理解链表
- void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
-
- // 单链表尾插
- void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//用二级指针,x为要插入的数据
-
- // 单链表的头插
- void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
-
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
-
- // 单链表头删
- void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
-
- // 单链表查找
- SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
-
- // 单链表在pos位置之前插入x(效率较低)(得传头指针)(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
-
- // 单链表删除pos位置之前的值(效率较低)(得传头指针)(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
-
- // 单链表在pos位置之后插入x,单链表比较适合这种
- void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
-
- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值,单链表比较适合这种
- void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
-
- // 不传头指针,在pos前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore1(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
-
- // 不传头指针,删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore1(SLTNode* pos);
-
- // 单链表的销毁,不传二级
- void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead);
-
- // 单链表的销毁,传二级
- void SLTDestroy1(SLTNode** pphead);
在SList.c下
- #include"SList.h"//别忘了
-
- //链表的打印
- void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
- {
- //assert(phead);这里并不需要断言phead不为空
- //为什么这里不需要断言?
- //空链表可以打印,即phead==NULL可以打印,直接断言就不合适了
- //那空顺序表也可以打印,那它为什么就要断言呢?
- //因为phead是指向第一个存有数据的结点的
- //而顺序表的ps是指向一个结构体
- SLTNode* cur = phead;//将phead赋值给cur,所以cur也指向第一个结点
- while (cur != NULL)//或while(cur)
- {
- printf("%d->", cur->data);//打印的时候加了个箭头更方便理解
- cur = cur->next;//next是下一个结点的地址
- //++cur/cur++;这种是不行的,指针加加,加到的是连续的下一个位置
- //链表的每一个结点都是单独malloc出来的,我们不能保证结点之间的地址是连续的
- }
- printf("NULL\n");
- }
-
- // 动态申请一个结点
- SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x)
- {
- //同样不需要断言
- SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//先创建个结点
- if (newnode == NULL)//如果malloc失败
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- return NULL;
- }
- //如果malloc成功
- newnode->data = x;//插入的数据
- newnode->next = NULL;//初始化为空
-
- return newnode;//返回newnode
- }
-
- // 单链表尾插
- void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
- //注意区分几个断言的判断,plist有可能是空,pphead一定不能为空
-
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- //找尾(尾插之前先找到尾)
- if (*pphead == NULL)//若链表为空
- {
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
- else//若链表不为空
- {
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- //对于不为空的链表:尾插的本质是原尾结点要存新尾结点的地址
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail->next = newnode;
- /*有些同学会写成:
- while (tail != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- tail = newnode;*/
- }
- }
-
-
- // 单链表的头插
- void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //发现plist不管是否为空,头插的方法都一样
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- newnode->next = *pphead;
- *pphead = newnode;
- }
-
- // 单链表的尾删
- void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //检查有无结点
- assert(*pphead != NULL);//或者写成assert(*pphead);
- //1.只有一个结点
- if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
- {
- free(*pphead);
- *pphead = NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- //2.有多个结点
- /*//法一:
- SLTNode* prev=NULL;
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next != NULL)
- {
- prev = tail;
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- free(tail);
- tail = NULL;
- prev->next = NULL;*/
- //法二:
- SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
- while (tail->next->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
-
- free(tail->next);
- tail->next = NULL;
- }
- }
-
- // 单链表头删
- void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
-
- //检查有无结点
- assert(*pphead != NULL);
-
- SLTNode* first = *pphead;
- *pphead = first->next;
- free(first);
- first = NULL;
- }
-
- // 单链表查找
- SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
- {
- SLTNode* cur = phead;//用cur去遍历,不用phead
- while (cur)//找x
- {
- if (cur->data == x)//如果找到了
- {
- return cur;
- }
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- return NULL;//如果找不到
- }
-
- //单链表在pos位置之前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);//默认pos一定会找到
- assert(pphead);//pphead是plist的地址,不能为空
- if (pos == *pphead)//如果pos在第一个位置——那就是头插
- {
- SLTPushFront(pphead, x);
- }
- else//如果pos不是第一个位置
- {
- //找到pos的前一个位置
- SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
- while (prev->next != pos)
- {
- prev = prev->next;
- }
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- prev->next = newnode;
- newnode->next = pos;
- }
- }
-
- // 单链表删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- assert(pos);
-
- if (*pphead == pos)//如果pos在第一个位置
- {
- SLTPopFront(pphead);//头删
- }
- else//如果不在第一个位置
- {
- SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
- while (prev->next != pos)
- {
- prev = prev->next;
- }
- prev->next = pos->next;
- free(pos);
- //pos = NULL;形参的改变不影响实参,加不加这句话都可以
- }
- }
-
- //单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
- SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
- newnode->next = pos->next;
- pos->next = newnode;
- }
-
- // 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
- void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- assert(pos->next);
-
- SLTNode* del = pos->next;//保存要删除的结点
- pos->next = pos->next->next;//或者写成pos->next=del->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
-
- // 不传头指针,在pos前插入x(也可以理解为在pos位置插入)
- void SLTInsertBefore1(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);
-
- //调用单链表在pos位置之后插入x的函数
- SLTInsertAfter(pos, x);
-
- //交换pos和pos->next的值
- SLTDataType temp;
- temp = pos->data;
- pos->data = pos->next->data;
- pos->next->data = temp;
- }
-
- // 不传头指针,删除pos位置之前的值(也可以理解为删除pos位置的值)
- void SLTEraseBefore1(SLTNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);
- assert(pos->next);//不能尾删
-
- SLTNode* del = pos->next;
- pos->data = pos->next->data;
- pos->next = pos->next->next;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
-
- // 单链表的销毁
- void SLTDestroy(SLTNode* phead)
- {
- SLTNode* cur = phead;
- /*//有些人一开始会这样写
- while (cur)
- {
- //free不是销毁这个指针指向的内存,而是将指针指向的内存还给操作系统
- free(cur);//cur依旧指向free之前的地址
- cur = cur->next;
- }*/
-
- while (cur)
- {
- SLTNode* tmp = cur->next;
- free(cur);
- cur = tmp;
- }
- }
-
- // 单链表的销毁,传二级
- void SLTDestroy1(SLTNode** pphead)
- {
- assert(pphead);
- SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
- while (cur)
- {
- SLTNode* tmp = cur->next;
- free(cur);
- cur = tmp;
- }
- *pphead = NULL;
- }
在Test.c下
- #include"SList.h"
-
- void TestSList1()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
-
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- void TestSList2()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopBack(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList3()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- SLTPopFront(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- void TestSList4()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //将寻找和修改结合
- //eg:值为2的结点*2
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- ret->data *= 2;
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList5()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //寻找值为2的结点
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertBefore(&plist, ret, 20);//在该结点前插入值为20的结点
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- }
-
- TestSList6()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- //寻找值为2的结点
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseBefore(&plist, ret);
- ret = NULL;//一般在这里置空
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList7()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertAfter(ret, 20);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList8()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseAfter(ret);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList9()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTInsertBefore1(ret, 20);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList10()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTNode* ret = SLTFind(plist, 2);
- SLTEraseBefore1(ret);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- TestSList11()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTDestroy(plist);
- plist = NULL;
- }
-
- TestSList12()
- {
- SLTNode* plist = NULL;
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
- SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
- SLTPrint(plist);
-
- SLTDestroy1(&plist);
- SLTPrint(plist);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- //TestSList1();
- //TestSList2();
- //TestSList3();
- //TestSList4();
- //TestSList5();
- //TestSList6();
- //TestSList7();
- //TestSList8();
- //TestSList9();
- //TestSList10();
- //TestSList11();
- TestSList12();
- return 0;
- }
欢迎指正❀